
The evolution of heat pipe technology is pivotal for efficient thermal management across various high-tech industries, including electronics, aerospace, and medical devices. With the increasing demand for compact, high-performance systems, understanding the principles and innovations in heat pipe design is essential for engineers and manufacturers.
Understanding Heat Pipes
Heat pipes are highly effective thermal management devices that utilize phase change and capillary action to transport heat with minimal temperature difference. They consist of a sealed container filled with a working fluid, which absorbs heat at one end (the evaporator), vaporizes, and then condenses at the cooler end (the condenser), releasing the absorbed heat. This cycle is facilitated by a wicking structure that returns the liquid to the evaporator, allowing for continuous operation without moving parts.
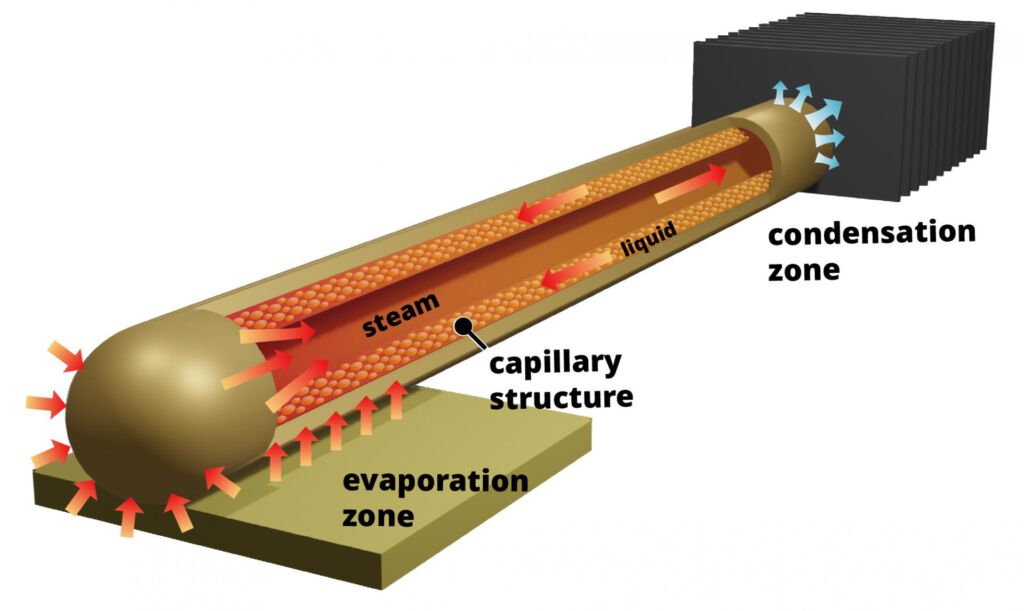
Mechanisms of Heat Transfer
Heat pipes operate through three primary mechanisms: phase change, conduction, and convection. The efficiency of heat pipes stems from their ability to maintain low thermal resistance while transferring significant amounts of heat over distances. This capability is particularly crucial in applications where traditional conduction methods fall short, such as in densely packed electronic components.
Applications Across Industries
The versatility of heat pipes makes them indispensable in various sectors:
- Electronics Cooling: Heat pipes are integral in managing thermal loads from CPUs and GPUs in laptops and servers, ensuring optimal performance without overheating.
- Aerospace: In spacecraft and satellites, heat pipes maintain critical temperatures under extreme conditions, enhancing reliability.
- Medical Equipment: Precision cooling in devices like MRI machines ensures accurate operation and patient safety.
- HVAC Systems: They are employed for energy-efficient heat recovery, optimizing temperature control in building systems.
Key Design Considerations
When designing heat pipes, several factors must be considered to optimize performance:
- Material Selection: Copper is favored for its high thermal conductivity and compatibility with common working fluids like water. Aluminum may be used in applications where weight and cost are more critical than thermal efficiency.
- Wick Structure: The design of the wick influences capillary action and fluid return rates. Advanced materials such as bi-porous sintered structures can enhance performance by improving fluid dynamics.
- Size and Shape: The dimensions of heat pipes must align with specific application requirements. For instance, flat heat pipes (or vapor chambers) are ideal for compact electronics due to their efficiency in space-constrained environments.
Innovations in Heat Pipe Technology
Recent advancements focus on enhancing thermal performance through innovative designs:
- Advanced Wick Structures: Utilizing ultra-fine fibers or novel materials can significantly improve capillary action, enabling faster heat transfer.
- Integration with Phase Change Materials: Incorporating phase change materials into heat pipe designs allows for better thermal responsiveness under varying loads.
- Custom Solutions: Tailored designs can address unique challenges in complex assembly spaces or extreme operating conditions, such as those found in aerospace applications.
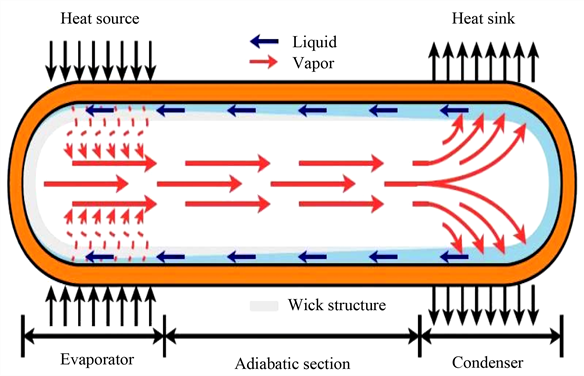
Challenges and Optimization Strategies
Despite their advantages, several challenges persist in heat pipe design:
- Operating Limitations: Misconceptions about uniform thermal conductivity across different lengths or orientations can lead to inefficiencies. Designers must account for these variables to enhance performance.
- System Integration: Effective integration with other system components is crucial. Careful consideration of bends and curvatures is necessary to avoid compromising heat transfer capabilities.
Utilizing computational fluid dynamics (CFD) modeling can aid in simulating performance under various conditions, ensuring that designs meet stringent operational requirements.
Conclusion
As industries continue to push the boundaries of technology, the role of heat pipes in thermal management becomes increasingly significant. By leveraging advanced design techniques and materials, engineers can develop robust solutions that meet the growing demands for efficiency and reliability in high-performance applications..
To-Team support team is at your service.
Please contact us using any of the following channels:
E-mail: [email protected]
Tel: +972.77.540.1143
